Carotid Disease (Carotid Stenosis)
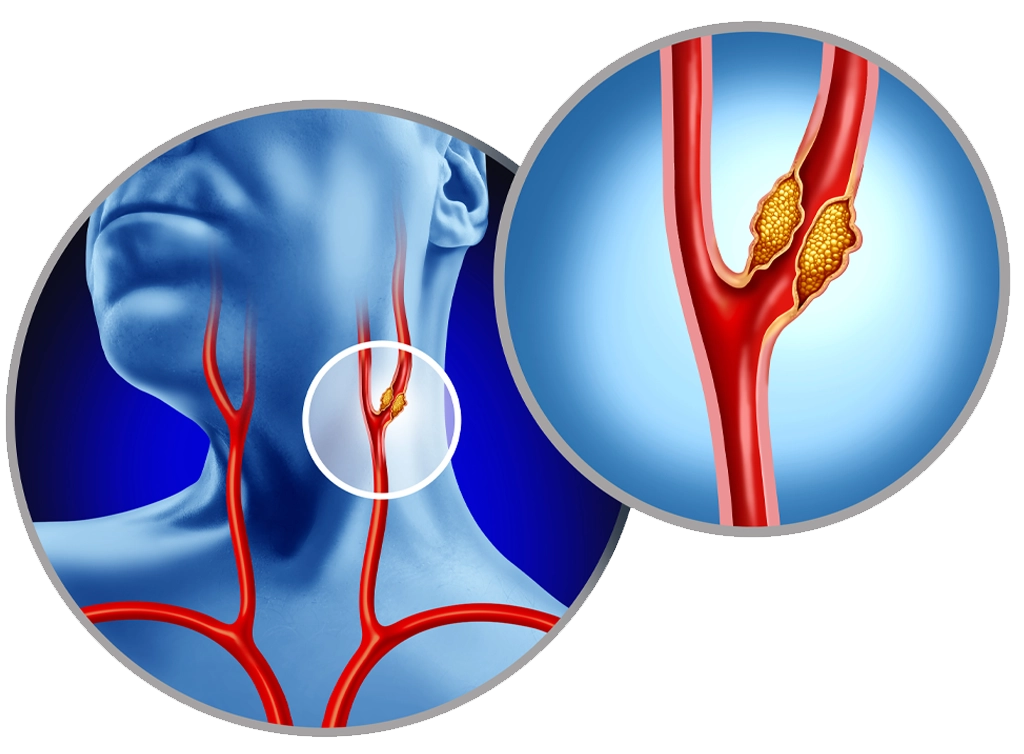
Your carotid arteries are the two main arteries that carry blood from your heart, up through your neck, to your brain. Healthy carotid arteries are smooth and allow blood to flow freely to the brain and provide oxygen, glucose, and other nutrients that your brain cells need.
With age, the carotid arteries build up plaque, a sticky substance made up mostly of fat and cholesterol. Calcium, clot and plaque narrows the passageway within the arteries and causes them to become stiff.
If left untreated, carotid disease may lead to stroke, where lack of oxygen and other essential nutrients cause damage to the brain. Strokes usually result when bits of plaque and clot break off from the blockage and flow to the brain. Depending on its severity, a stroke can cause major disability or even be fatal. In fact, strokes are the third leading cause of death in the United States and the leading cause of permanent disability in older adults.